 Flag of Zambia Flag of Zambia
|
|
|
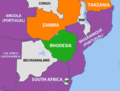
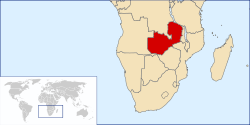
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa. It is bordered to the north by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country.
Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. Following European expeditions in the eighteenth century, Britain colonised the region, forming the British protectorates of Barotziland–North-Western Rhodesia and North-Eastern Rhodesia towards the end of the nineteenth century. These were merged in 1911 to form Northern Rhodesia. For most of the colonial period, Zambia was governed by an administration appointed from London with the advice of the British South Africa Company.
On 24 October 1964, Zambia became independent of the United Kingdom as a republic in the Commonwealth, and prime minister Kenneth Kaunda became the inaugural president. Kaunda's socialist United National Independence Party (UNIP) maintained power from 1964 until 1991 with him playing a key role in regional diplomacy, cooperating closely with the United States in search of solutions to conflicts in Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. From 1972 to 1991, Zambia was a one-party state with UNIP as the sole legal political party under the motto "One Zambia, One Nation" coined by Kaunda. Kaunda was succeeded by Frederick Chiluba of the social-democratic Movement for Multi-Party Democracy in 1991, beginning a period of socio-economic development and government decentralisation. Zambia has since become a multi-party state and has experienced several peaceful transitions of power.
Zambia contains abundant natural resources, including minerals, wildlife, forestry, freshwater, and arable land. As of the latest estimate in 2018, 47.9 percent of the population is affected by multidimensional poverty. The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is headquartered in Lusaka. (Full article...)
Mainza Mathias Chona (21 January 1930 – 11 December 2001) was a Zambian politician and founder of UNIP who served as the third vice-president of Zambia from 1970 to 1973 and Prime Minister on two occasions: from 25 August 1973 to 27 May 1975 and from 20 July 1977 to 15 June 1978.
He was Secretary General of the United National Independence Party (UNIP), the ruling party, from 1978 to 1981. This position was the de facto second in command in the hierarchy of Zambian politics during the period of the One Party Participatory State (1973–1991). (Full article...)
The following are images from various Zambia-related articles on Wikipedia.
-
Image 1Ingombe Ilede trading post in Southern Zambia. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 2Nsima (top right corner) with three types of relish. (from Zambia)
-
Image 3Density map of dominant regional languages (from Zambia)
-
Image 4An 1864 photograph of the Scottish explorer and missionary David Livingstone (from Zambia)
-
Image 5Zambia map of Köppen climate classification (from Zambia)
-
Image 6Pupils at the St Monica's Girls Secondary School in Chipata, Eastern Province (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 8The Mwata Kazembe opens the Mutomboko ceremony (from Zambia)
-
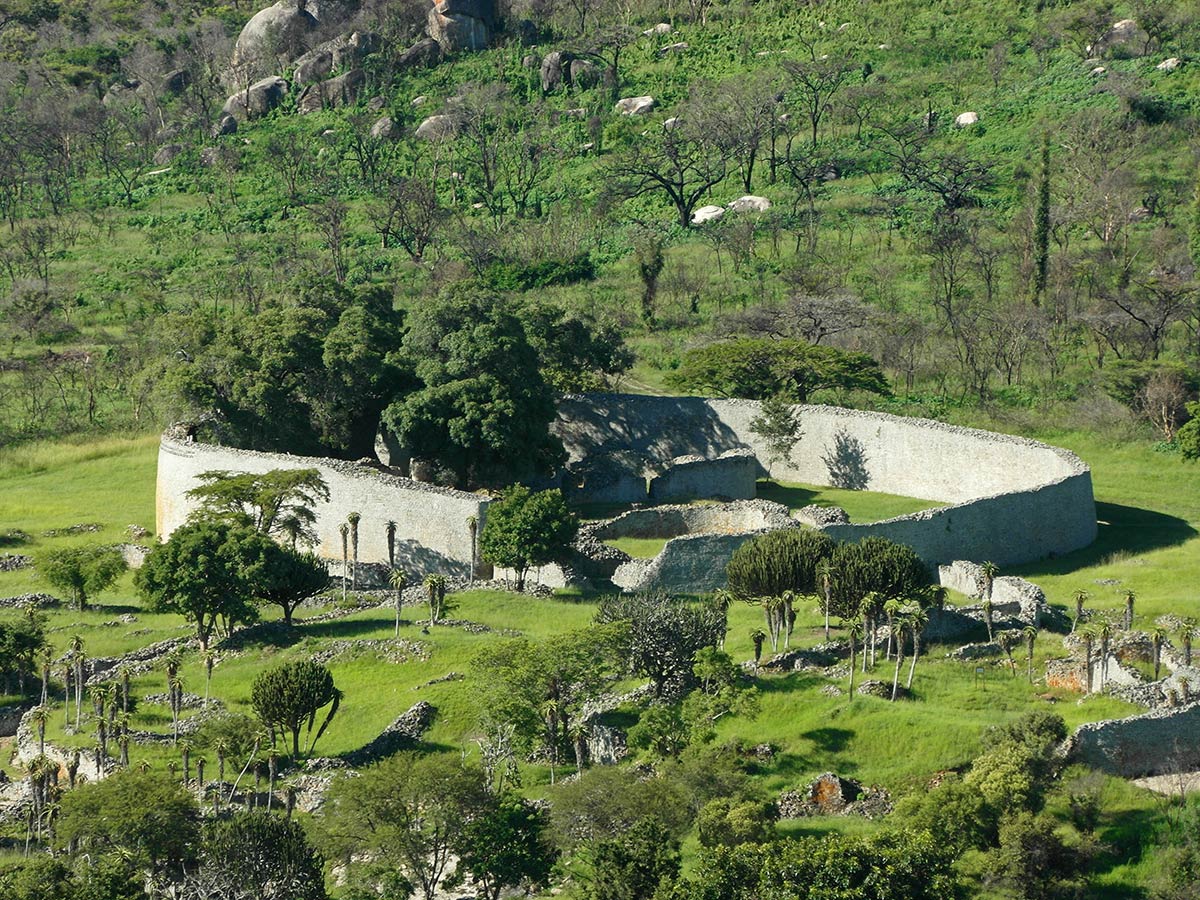
Image 9Ruins of Great Zimbabwe, Kalanga/ Shona rulers of this Kingdom dominated trade at Ingombe Ilede. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 10The kalonga (ruler) of the Chewa today descends from the kalonga of the Maravi Empire (from Zambia)
-
Image 11Drawing of the ruler of Lunda, Mwata Kazembe, receiving Portuguese in the royal courtyard in the 1800s (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 13Zambia National Assembly building in Lusaka (from Zambia)
-
Image 14Lukasa memory board, was used by members of Mbudye (an association of groits in charge of maintaining Baluba history) (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 15Pupils at the St Monica's Girls Secondary School in Chipata, Eastern Province (from Zambia)
-
Image 16Zambia map of Köppen climate classification (from Zambia)
-
Image 17Ancient (but graffitied) Rock Art in Nsalu Cave, Kasanka National Park in North-Central Zambia (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 19Inside the palace of the Litunga, ruler of the Lozi. Due to the flooding on the Zambezi, the Litunga has two palaces one of which is on higher ground. The movement of Litunga to higher land is celebrated at the Kuomboka Ceremony (from Zambia)
-
Image 20Inside the palace of the Litunga, ruler of the Lozi. Due to the flooding on the Zambezi, the Litunga has two palaces one of which is on higher ground. The movement of Litunga to higher land is celebrated at the Kuomboka Ceremony (from History of Zambia)
-
-
Image 22S.M Chisembele, Cabinet Minister, Western Province (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 23A drawing of Lunda houses by a Portuguese visitor. The size of the doorways relative to the building emphasizes the scale of the buildings (from Zambia)
-
Image 24Batonga fisherwomen in Southern Zambia. Women have played and continue to play pivotal roles in many African societies (from Zambia)
-
Image 25Drawing of the ruler of Lunda, Mwata Kazembe, receiving Portuguese in the royal courtyard in the 1800s (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 26Stamp with portrait of Queen Elizabeth II, 1955 (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 27Ancient (but graffitied) Rock Art in Nsalu Cave, Kasanka National Park in North-Central Zambia. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 28The major Nkana open copper mine, Kitwe. (from Zambia)
-
Image 29GDP per capita (current), compared to neighbouring countries (world average = 100) (from Zambia)
-
Image 30Three young Ngoni chiefs. The Ngoni made their way into Eastern Zambia from KwaZulu in South Africa. They eventually assimilated into the local ethnic groups. (from Zambia)
-
Image 31Ruins of Great Zimbabwe. Kalanga/ Shona rulers of this kingdom dominated trade at Ingombe Ilede (from Zambia)
-
Image 32The Kalonga of the Chewa today descends from the Kalonga (rulers) of the Maravi Empire. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 33Batonga fisherwomen in Southern Zambia. Women have played and continue to play pivotal roles in many African societies (from Zambia)
-
Image 34The kalonga (ruler) of the Chewa today descends from the kalonga of the Maravi Empire (from Zambia)
-
Image 35The official national animal of Zambia is the African fish eagle (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 37Three young Ngoni chiefs. The Ngoni made their way into Eastern Zambia from KwaZulu in South Africa. They eventually assimilated into the local ethnic groups. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 38Kenneth Kaunda, first president, on a state visit to Romania in 1970 (from Zambia)
-
Image 39A Yombe sculpture, 19th century. (from Zambia)
-
Image 40GDP per capita (current), compared to neighbouring countries (world average = 100) (from Zambia)
-
Image 41Nsima (top right corner) with three types of relish. (from Zambia)
-
Image 42Enormous Ba-Ila settlement. These communities have been of interest to mathematicians due to their fractal pattern design. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 43Ancient (but graffitied) Rock Art in Nsalu Cave, Kasanka National Park in North-Central Zambia (from Zambia)
-
Image 44An 1864 photograph of the Scottish explorer and missionary David Livingstone (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 46Inside the palace of the Litunga, ruler of the Lozi. Due to the flooding on the Zambezi, the Litunga has two palaces one of which is on higher ground. The movement of Litunga to higher land is celebrated at the Kuomboka Ceremony (from Zambia)
-
Image 47The major Nkana open copper mine, Kitwe. (from Zambia)
-
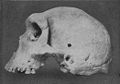
Image 48Skull of Broken Hill Man discovered in present-day Kabwe. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 49Tribal and linguistic map of Zambia (from Zambia)
-
Image 50President Edgar Lungu with Russian President Vladimir Putin, 26 July 2018 (from Zambia)
-
Image 51Seated female Staffs of office (Kibango), were displayed by Luba kings. In Luba society, women's bodies were considered the ultimate vessels of spiritual power. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 52Tribal and linguistic map of Zambia (from Zambia)
-
Image 53A drawing of Lunda houses by a Portuguese visitor. The size of the doorways relative to the building emphasizes the scale of the buildings (from Zambia)
-
Image 54The Mwata Kazembe opens the Mutomboko ceremony (from Zambia)
-
Image 55The geopolitical situation during the Rhodesian Bush War in 1965 – countries friendly to the nationalists are coloured orange (from Zambia)
-
Image 56Three young Ngoni chiefs. The Ngoni made their way into Eastern Zambia from KwaZulu in South Africa. They eventually assimilated into the local ethnic groups. (from Zambia)
-
Image 57Density map of dominant regional languages (from Zambia)
-
Image 58Ruins of Great Zimbabwe. Kalanga/ Shona rulers of this kingdom dominated trade at Ingombe Ilede (from Zambia)
-
Image 59Zambia National Assembly building in Lusaka (from Zambia)
-
-
Image 61Batonga fisherwomen in Southern Zambia. Women have and continue to play important roles in many African societies. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 62President Edgar Lungu with Russian President Vladimir Putin, 26 July 2018 (from Zambia)
-
Image 63Makishi dancer, found in North-Western Zambia, represent spirits of a deceased who returns to assist the living (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 64Ila Headman's son in Southern Zambia, Cattle formed an important part of their society. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 65The official national animal of Zambia is the African fish eagle (from Zambia)
-
Image 66A Yombe sculpture, 19th century. (from Zambia)
-
Image 67Drawing of the ruler of Lunda, Mwata Kazembe, receiving Portuguese in the royal courtyard in the 1800s (from Zambia)
-
Image 68Kenneth Kaunda, first president, on a state visit to Romania in 1970 (from Zambia)
-
Image 69A drawing of Lunda houses by a Portuguese. The size of the doorways relative to the building emphasizes the scale of the buildings. (from History of Zambia)
-
Image 70The geopolitical situation during the Rhodesian Bush War in 1965 – countries friendly to the nationalists are coloured orange (from Zambia)
This is a Good article, an article that meets a core set of high editorial standards. John Harrison Clark III or Changa-Changa (10 May 1860 – 9 December 1927) was an Anglo-South African explorer and adventurer who effectively ruled much of what is today southern Zambia from the early 1890s to 1902. He arrived alone from South Africa in about 1887, reputedly as an outlaw, and assembled and trained a private army of Senga natives that he used to drive off various bands of slave-raiders. He took control of a swathe of territory on the north bank of the Zambezi river, became known as Chief "Changa-Changa" and, through a series of treaties with local chiefs, gained mineral and labour concessions covering much of the region.
Starting in 1897, Clark attempted to secure protection for his holdings from the British South Africa Company. The Company took little notice of him. A local chief, Chintanda, complained to the Company in 1899 that Clark had secured his concessions while passing himself off as a Company official and had been collecting hut tax for at least two years under this pretence. The Company resolved to remove him from power, and did so in 1902. Clark then farmed for about two decades, with some success, and moved in the late 1910s to Broken Hill. There he became a prominent local figure, and a partner in the first licensed brewery in Northern Rhodesia. Remaining in Broken Hill for the rest of his life, he died there in 1927. (Full article...)
 Category puzzle
Select [►] to view subcategories
| Topics related to Zambia
|
| Cities
|
Lusaka • Kitwe • Ndola • Kabwe • Chingola • Mufulira • Livingstone • Luanshya • Kasama • Chipata • Chililabombwe • Solwezi
|
| History
|
Bibliography of the history of Zambia • Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia •
The Africa House • British South Africa Company • Copperbelt strike (1935) • East African Campaign (World War I) • Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland • Governor-General of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland • Governor of Northern Rhodesia • History of Church activities in Zambia • Luapula Province border dispute • Lunda Empire • Mulungushi • Mwata Yamvo • North-Eastern Rhodesia • Northern Rhodesia • Northern Rhodesian African National Congress • North-Western Rhodesia • Rhodesian Man • Stairs Expedition • Zambia Independence Act
|
| Politics
|
Defence Force • Diplomatic missions • Elections • Foreign relations • Ministry of Health • Lusaka Declaration • National Assembly • Presidents • Prime Ministers • Political parties
|
| Provinces
|
Central • Copperbelt • Eastern • Luapula • Lusaka • North-Western • Northern • Southern • Western
• Muchinga Province
|
| Geography
|
Barotseland • Congo Pedicle • Dambos • Districts of Zambia • Kariba Gorge • Mporokoso Group • Nyika Plateau • Southern Africa • Rift Valley lakes • Zambezi Escarpment
|
| Economy
|
Bank of Zambia • Copperbelt • List of Zambian companies • Lusaka Stock Exchange • Zambian kwacha • Mount Makulu Zambia • Tazama Pipeline • Konkola Copper Mines • Zambia Consolidated Copper Mines • Zambia Post • Zambian Airways • Zamtel • Zambian pound • Rhodesia and Nyasaland pound
|
| Languages
|
Bemba language • Chichewa language • Cilungu • Fanagalo • Kaonde language • Lamba language • Lozi language • Lunda language • Mambwe language • Mbunda language • Shona language • Tonga language (Zambia) • Tumbuka language • Yauma language • Luvale language
|
| Culture
|
2011 All-Africa Games
Zambian traditional ceremonies
|
| Education
|
|
| Transport
|
Zambian Airways • Benguela railway • TAZARA Railway • Zambia Railways • Trans–Caprivi Highway • Great East Road (Zambia) • Great North Road (Zambia)
|
| Categories
|
Archaeological sites, Architecture, Cities, Communications, Conservation, Culture, Economy, Education, Geography, Government, Health, History, Media, Military, Lists, Law, People, Politics, Religion, Science and technology, Society, Sports, Provinces, Tourism, Transport, Zambia stubs
|
General:
Wikipedias in Zambian languages:
- Expand stub articles on Zambia-related topics.
|