The Solar System Portal
 The Sun and planets of the Solar System (distances not to scale)
The Sun and planets of the Solar System (distances not to scale)
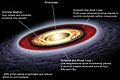
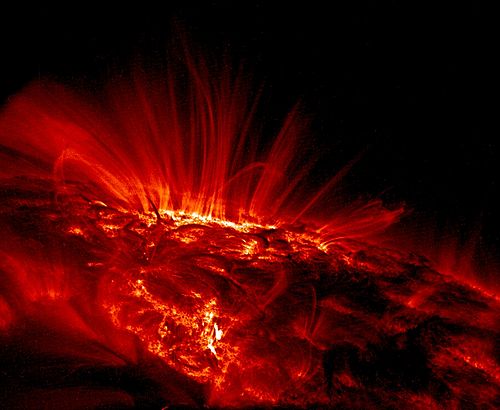
The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the masses that orbit it, most prominently its eight planets, of which Earth is one. The system formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, creating the Sun and a protoplanetary disc from which the orbiting bodies assembled. Inside the Sun's core hydrogen is fused into helium for billions of years, releasing energy which is over even longer periods of time emitted through the Sun's outer layer, the photosphere. This creates the heliosphere and a decreasing temperature gradient across the Solar System.
The mass of the Solar System is by 99.86% almost completely made up of the Sun's mass. The next most massive objects of the system are the eight planets, which by definition dominate the orbits they occupy. Closest to the Sun in order of increasing distance are the four terrestrial planets – Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. These are the planets of the inner Solar System. Earth and Mars are the only planets in the Solar System which orbit within the Sun's habitable zone, in which the sunlight can make surface water under atmospheric pressure liquid. Beyond the frost line at about five astronomical units (AU), are two gas giants – Jupiter and Saturn – and two ice giants – Uranus and Neptune. These are the planets of the outer Solar System. Jupiter and Saturn possess nearly 90% of the non-stellar mass of the Solar System.
Additionally to the planets there are in the Solar System other planetary-mass objects, but which do not dominate their orbits, such as dwarf planets and planetary-mass moons. The International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Center lists Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Makemake, and Haumea as dwarf planets. Four other Solar System objects are generally identified as such: Orcus, Quaoar, Gonggong, and Sedna. Natural satellites, which are commonly called 'moons', can be found throughout the Solar System and in sizes from planetary-mass moons to much less massive moonlets at their smallest. The largest two moons (Ganymede of Jupiter and Titan of Saturn) are larger than the smallest planet (Mercury), while the seven most massive, which includes Earth's Moon, are more massive and larger than any of the dwarf planets. Less massive than these planetary-mass objects are the vast number of small Solar System bodies, such as asteroids, comets, centaurs, meteoroids, and interplanetary dust clouds. All dwarf planets and many of the smaller bodies are within the asteroid belt (between Mars's and Jupiter's orbit) and the Kuiper belt (just outside Neptune's orbit).
The Solar System is within the heliosphere constantly flooded by the charged plasma particles of the solar wind, which forms with the interplanetary dust, gas and cosmic rays between the bodies of the Solar System an interplanetary medium. At around 70–90 AU from the Sun, the solar wind is halted by the interstellar medium, resulting in the heliopause and the border of the interplanetary medium to interstellar space. Further out somewhere beyond 2,000 AU from the Sun extends the outermost region of the Solar System, the theorized Oort cloud, the source for long-period comets, stretching to the edge of the Solar System, the edge of its Hill sphere, at 178,000–227,000 AU (2.81–3.59 ly), where its gravitational potential becomes equal to the galactic potential. The Solar System currently moves through a cloud of interstellar medium called the Local Cloud. The closest star to the Solar System, Proxima Centauri, is 269,000 AU (4.25 ly) away. Both are within the Local Bubble, a relatively small 1,000 light-years (ly) wide region of the Milky Way. (Full article...)
Selected article –
Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south divide, the Martian dichotomy, with the northern hemisphere mainly consisting of relatively flat, low lying plains, and the southern hemisphere of cratered highlands. Geologically, the planet is fairly active with marsquakes trembling underneath the ground, but also hosts many enormous volcanoes that are extinct (the tallest is Olympus Mons, 21.9 km or 13.6 mi tall), as well as one of the largest canyons in the Solar System (Valles Marineris, 4,000 km or 2,500 mi long). Mars has two natural satellites that are small and irregular in shape: Phobos and Deimos. With a significant axial tilt of 25 degrees, Mars experiences seasons, like Earth (which has an axial tilt of 23.5 degrees). A Martian solar year is equal to 1.88 Earth years (687 Earth days), a Martian solar day (sol) is equal to 24.6 hours. (Full article...)
Selected picture
General images
The following are images from various Solar System-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know –
- ...that New York's Panther Mountain (pictured) was the site of a prehistoric meteor crash?
- ...that the Beethoven crater in the Beethoven quadrangle on Mercury is the eleventh largest named impact crater in the Solar System?
- ...that the planet Mars appears red primarily because of a ubiquitous layer of dust containing nanophase ferric oxides?
- ...that the 1997 volcanic eruption of Pillan Patera on Jupiter's moon Io was the largest effusive eruption ever witnessed?
- ...that the Caloris Basin on Mercury, one of the largest impact basins in the Solar System, is surrounded by a series of geological formations believed to have been produced by the basin's ejecta?
- ...that Kordylewski clouds are large concentrations of dust that orbit Earth at the distance of the Moon?
- ...that no viable solution has yet been found to counteract radiation from space, which is a serious threat to astronauts on any future mission to Mars?
- ...that Claudia Alexander was the last project manager of NASA's Galileo mission to Jupiter?
Categories
| Solar System | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Celestial mechanics | Comets | ...in fiction |

|

| |
| Minor planets | Moons | Planetary missions |

|

|

|
| Planets... | Sun | Surface feature nomenclature... |
This article is sourced from Wikipedia. Content is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.



























![Image 6Diagram of the Local Interstellar Cloud, the G-Cloud and surrounding stars. As of 2022[update], the exact position of the Solar System within the interstellar clouds remains an unresolved question in astronomy. (from Solar System)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7c/The_Local_Interstellar_Cloud_and_neighboring_G-cloud_complex.svg/120px-The_Local_Interstellar_Cloud_and_neighboring_G-cloud_complex.svg.png)